Old Browser
BD Pharmingen™ Ac-DEVD-AFC Caspase-3 Fluorogenic Substrate

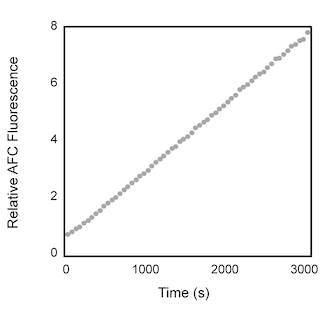
Activity of recombinant human caspase-3. Ac-DEVD-AFC (MW 729 Daltons) is a synthetic tetrapeptide substrate that is cleaved between D and AFC, releasing the fluorogenic AFC, which is detected by spectrofluorometry. When coupled to an aldehyde group (CHO), the DEVD tetrapeptide functions as a potent inhibitor of caspase activity and can be used to block caspase cleavage of Ac-DEVD-AFC. Left panel: In the presence of active caspase-3, fluorogenic AFC is released from Ac-DEVD-AFC, demonstrating the activity of caspase-3 enzyme. Right panel: In the presence of both active caspase-3 and Ac-DEVD-CHO, fluorogenic AFC is not released, indicating that Ac-DEVD-AFC was not cleaved and that caspase-3 activity was blocked by Ac-DEVD-CHO.


Activity of recombinant human caspase-3. Ac-DEVD-AFC (MW 729 Daltons) is a synthetic tetrapeptide substrate that is cleaved between D and AFC, releasing the fluorogenic AFC, which is detected by spectrofluorometry. When coupled to an aldehyde group (CHO), the DEVD tetrapeptide functions as a potent inhibitor of caspase activity and can be used to block caspase cleavage of Ac-DEVD-AFC. Left panel: In the presence of active caspase-3, fluorogenic AFC is released from Ac-DEVD-AFC, demonstrating the activity of caspase-3 enzyme. Right panel: In the presence of both active caspase-3 and Ac-DEVD-CHO, fluorogenic AFC is not released, indicating that Ac-DEVD-AFC was not cleaved and that caspase-3 activity was blocked by Ac-DEVD-CHO.

Activity of recombinant human caspase-3. Ac-DEVD-AFC (MW 729 Daltons) is a synthetic tetrapeptide substrate that is cleaved between D and AFC, releasing the fluorogenic AFC, which is detected by spectrofluorometry. When coupled to an aldehyde group (CHO), the DEVD tetrapeptide functions as a potent inhibitor of caspase activity and can be used to block caspase cleavage of Ac-DEVD-AFC. Left panel: In the presence of active caspase-3, fluorogenic AFC is released from Ac-DEVD-AFC, demonstrating the activity of caspase-3 enzyme. Right panel: In the presence of both active caspase-3 and Ac-DEVD-CHO, fluorogenic AFC is not released, indicating that Ac-DEVD-AFC was not cleaved and that caspase-3 activity was blocked by Ac-DEVD-CHO.


BD Pharmingen™ Ac-DEVD-AFC Caspase-3 Fluorogenic Substrate

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Reconstitute the Ac-DEVD-AFC substrate with 1 ml DMSO before use. The reconstituted substrate may be stored in small aliquots at -20°C.Store the reconstituted Ac-DEVD-AFC substrate at –20°C for up to two months.
Recommended Assay Procedures
The Ac-DEVD-AFC fluorogenic substrate may be used in protease assays, such as those described by Nicholson et al and Mashima et al . When Ac-DEVD-AFC is treated with apoptotic cell lysates or with purified, active caspase-3, AFC is released. AFC release can be monitored in a spectrofluorometer at an excitation wavelength of 400 nm and an emission wavelength range of 480-520 nm. Apoptotic cell lysates yield a considerable emission as compared to non-apoptotic cell lysates or apoptotic lysates which also contain Ac-DEVD-CHO. The amount of cell lysate required for protease assays will vary between experimental systems and should be optimized by the investigator.
Ac-DEVD-AFC Protease Assay
The Protease Assay protocol can be used to measure caspase-3 activity using the Ac-DEVD-AFC, Caspase-3 Fluorogenic Substrate (Cat. No. 556574).
Materials Required
1. Purified, Active Recombinant Caspase-3 (Cat. No. 556472): Not Included . 5 µg enzyme in 25 µl. The enzyme is buffered with 50 mM Tris, pH 8.0, with 100 mM NaCl and 50 mM imidazole.
2. Ac-DEVD-AFC (Cat. No. 556574): Included . 1 mg peptide in DMSO; lyophilized. Reconstitute in 1 ml DMSO to yield 1 mg/ml peptide.
3. Ac-DEVD-CHO (Cat. No. 556465): Not Included . 1 mg peptide in DMSO; lyophilized. Reconstitue in 1 ml DMSO to yield 1 mg/ml peptide.
4. Protease assay buffer: 20 mM PIPES, 100 mM NaCl, 10 mM DTT, 1 mM EDTA, 0.1% (w/v) CHAPS, 10% sucrose, pH 7.2.
Procedure
1. To one tube, add 10 µl of Ac-DEVD-AFC into 1 ml of assay buffer. In a separate tube, add 10 µl of Ac-DEVD-AFC and 1 µl Ac-DEVD-CHO into 1 ml assay buffer.
2. Add 50 ng purified, active caspase-3 to each tube.
3. Incubate for 1 hour at 37°C.
4. Measure the AFC liberated from the Ac-DEVD-AFC using a spectrofluorometer with an excitation wavelength of 400 nm and an emission wavelength of 480 - 520 nm (peak at 505 nm).
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products
The caspase family of cysteine proteases was discovered following a search of human cDNA libraries for sequences homologous to ced -3, a cell death gene described in the nematode worm C. elegans . The first mammalian homologue of ced -3 to be identified was ICE (interleukin-1 β converting enzyme). Subsequently, numerous mammalian ced -3 homologues have been discovered and have each been given a variety of names. To achieve consistency, the term "caspase" was adopted as a root name for all family members. The name reflects the catalytic properties of these enzymes, the "c" denotes their cysteine protease mechanism and "aspase" refers to their ability to cleave after aspartic acid residues. These proteases are expressed as inactive proenzymes, which are proteolytically cleaved into large and small subunits, which form the active enzyme. Active caspase-3 consists of 17 and 12 kDa subunits which are derived from a 32 kDa proenzyme (pro-caspase-3). Active caspase-3 has been shown to cleave PARP [poly (ADP ribose) polymerase], an enzyme that is involved in DNA repair and genomic maintenance. Proteolysis of the 116 kDa intact form of PARP into 85 and 25 kDa subunits results in loss of normal PARP function. The cleavage site in PARP is C-terminal to Asp-216. The upstream sequence of the PARP cleavage site, DEVD (Asp-Glu-Val-Asp), is utilized as a basis for the highly specific caspase-3 substrate Ac(N-acetyle)-DEVD-AFC (7-amino-4-trifluoromethylcoumarin). Caspase-3 cleaves the tetrapeptide between D and AFC, thus releasing the fluorogenic AFC which can be quantified by U.V. spectrofluorometry. When coupled to an aldehyde group (CHO), the DEVD peptide functions as a potent inhibitor of caspase-3 activity and can be used to block caspase-3 mediated cleavage of Ac-DEVD-AFC. These tetrapeptide substrates can be used to identify and quantitate caspase-3 activity in apoptotic cell lysates.
Development References (3)
-
Mashima T, Naito M, Kataoka S, Kawai H, Tsuruo T. Aspartate-based inhibitor of interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme prevents antitumor agent-induced apoptosis in human myeloid leukemia U937 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995; 209(3):907-915. (Biology: Functional assay). View Reference
-
Nicholson DW, Ali A, Thornberry NA, et al. Identification and inhibition of the ICE/CED-3 protease necessary for mammalian apoptosis. Nature. 1995; 376(6535):17-18. (Biology: Functional assay). View Reference
-
Patel T, Gores GJ, Kaufmann SH. The role of proteases during apoptosis. FASEB J. 1996; 10(5):587-597. (Biology: Functional assay). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.