Old Browser
Overview
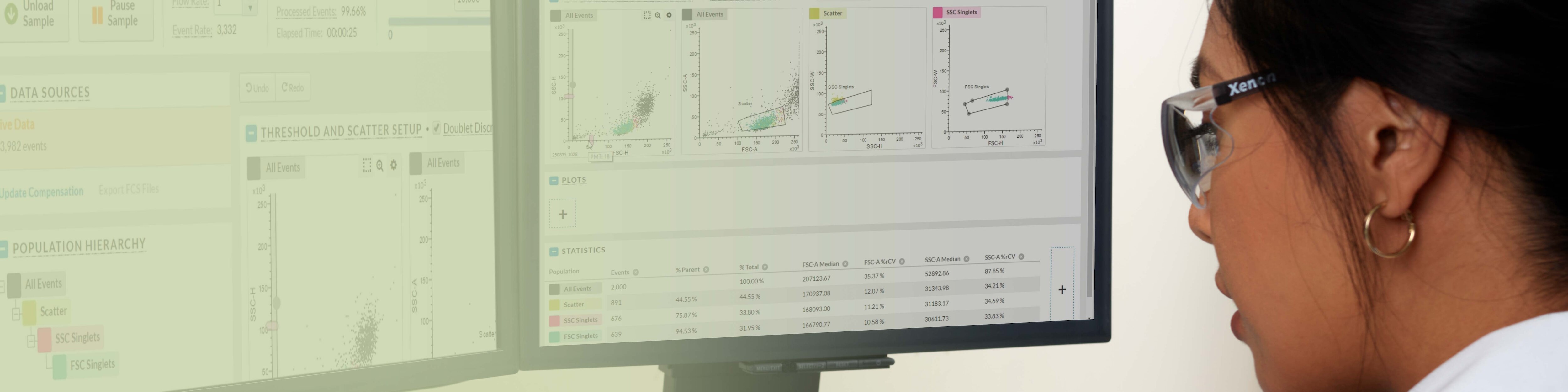
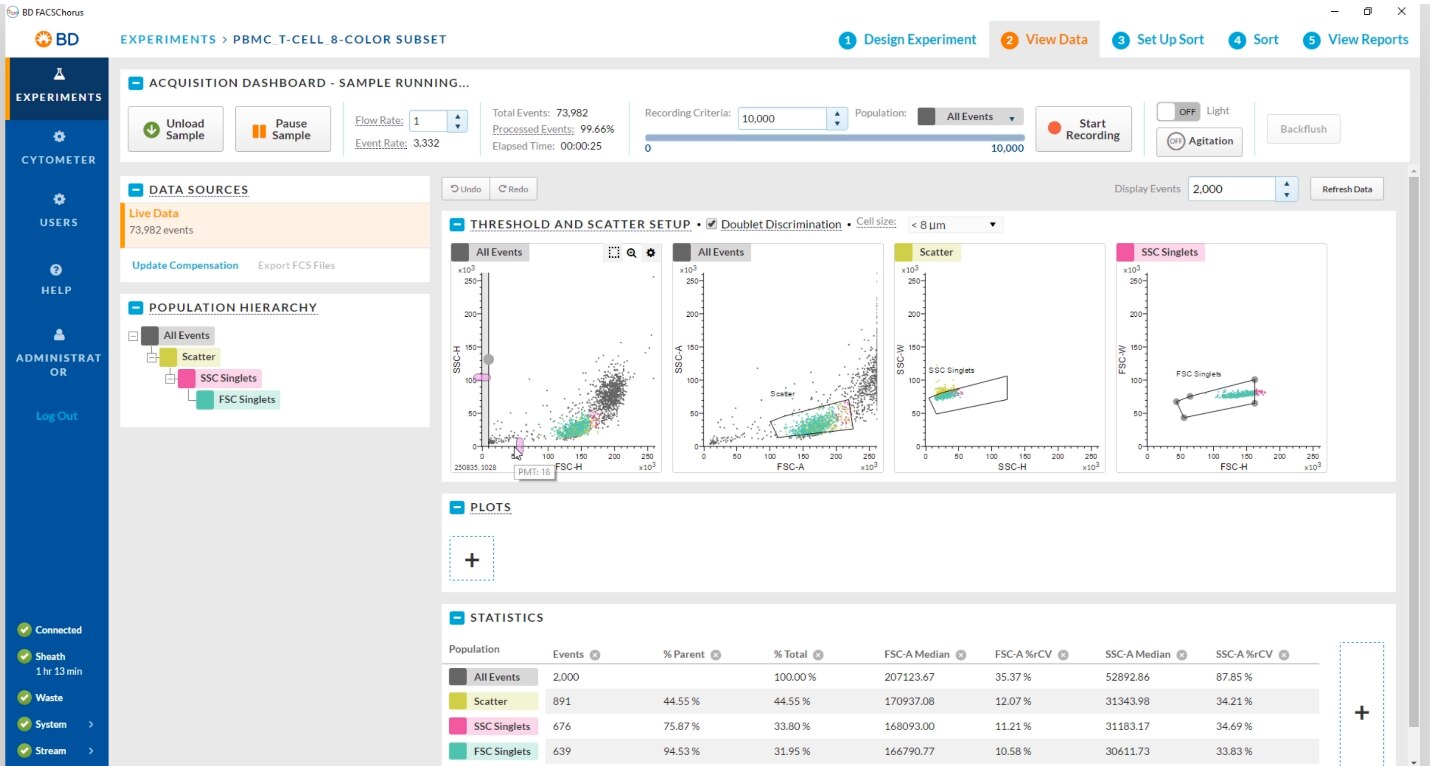
BD FACSChorus™ Software simplifies sorting by using a streamlined workflow that eliminates manual setup and monitoring so that you can focus on the science.
The software guides you through the entire cell sorting process by using advanced automation technology that improves throughput and minimizes downtime to promote experimental success.
Features
BD FACSChorus™ Software design is intuitive and easy to use so that even a new user can become proficient at sorting quickly.

Features include:
- Automated setup of laser delay, drop delay and side streams
- An interface that leads you through workflows
- On-screen instructions
- Index sorting acquisition and analysis
- Default plots and sort gates
- Prevention of tube overflow
- Automatically turned on deflection plates (only when necessary) to guard operator safety
- FCS 3.1 compatibility
- Proven BD FACS™ Accudrop and BD® Sweet Spot technology
Applications
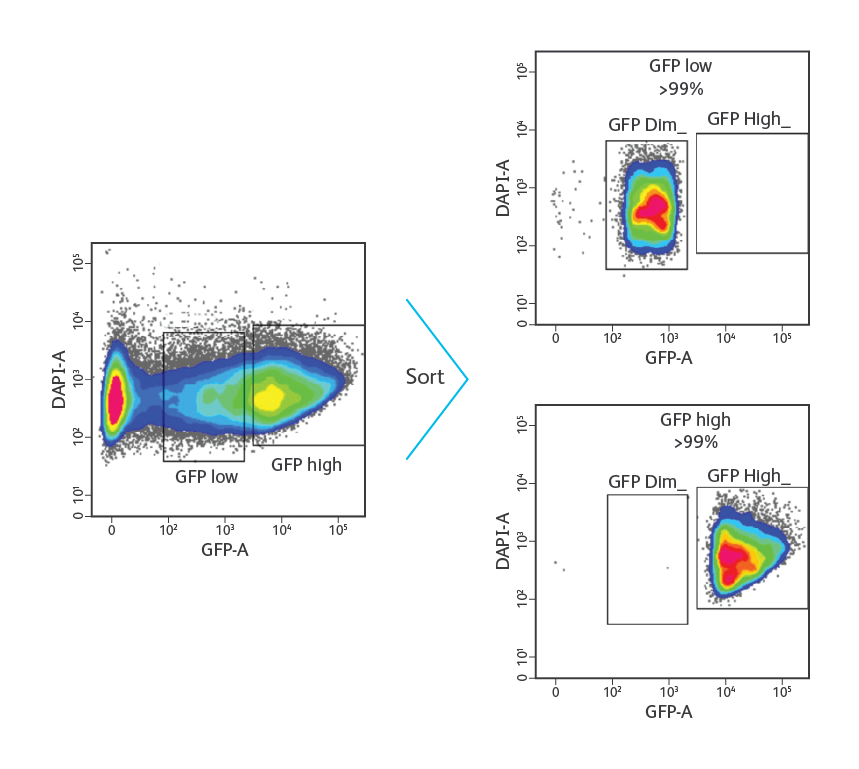
HEK-293 cells were transfected with 0.25 μg of pAcGFP (Clontech) vector and analyzed for the expression of GFP. Cells expressing variable levels of GFP could be clearly resolved. DAPI was used for exclusion of dead cells. Gates were drawn to identify and sort cells expressing low and high levels of GFP at 1,000 events/second in purity mode. Post-sort analysis revealed purity >99% for both sorted populations.
HEK-293 cells were fixed with 70% ethanol and stained with 0.5 μg/mL of DAPI.
(A) Population hierarchy. Area, height and width parameters for side scatter, forward scatter and DAPI were sequentially used to exclude doublets and cell aggregates. The gating strategy used in this experiment may have underestimated or excluded mitotic figures.
(B) DNA content analysis. Cells within the DAPI singlet gate showed DNA content between 2N and 4N, thus confirming exclusion of >4N doublets or aggregates.
(C) Post-sort validation of single-cell deposition. Cells within the DAPI singlet gate were sorted into three 96-multiwell plates with 99.7% single-cell deposition efficiency. Microscopy was used to confirm the presence of one cell per well. A representative image of a well containing one cell is shown.

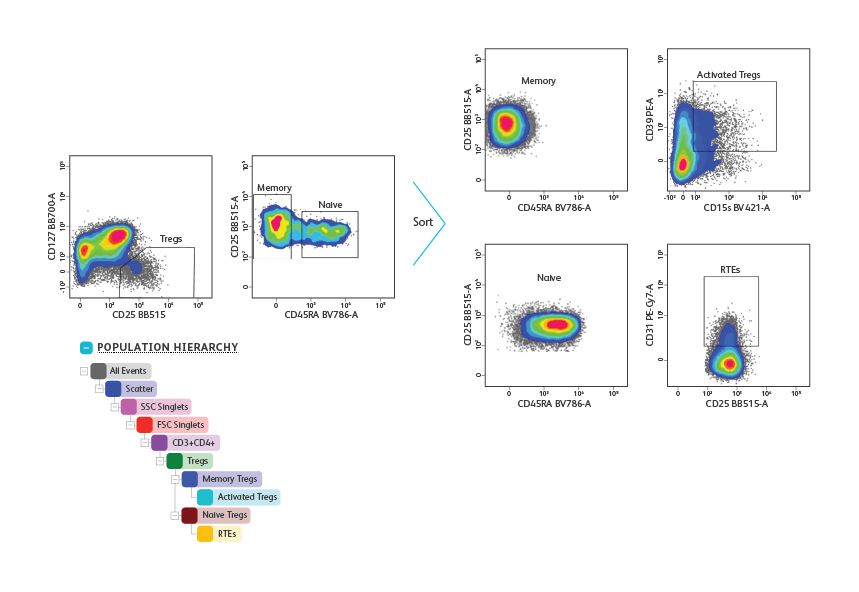
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated from a healthy donor and stained with a cocktail of surface markers (CD3, CD4, CD25, CD127 and CD45RA) for the detection and purification of Treg subsets. Lymphocytes and singlets were first gated based on light scatter properties followed by gating of CD3+CD4+ T cells (not shown). Tregs were then identified as CD127low/neg CD25high. From the Treg gate, CD45RA+ naïve and CD45RA– memory Tregs were identified and sorted at 5,000 events/sec in purity mode. Post-sort analysis revealed homogenous populations of memory and naïve Tregs. Purified cells were then stained for additional surface markers (CD31, CD39 and CD15s) for immunophenotyping. CD31+ recent thymic emigrants (RTEs) were detected within CD45RA+ naïve Tregs, whereas highly activated Tregs were detected within CD45RA– memory Tregs.
Splenocytes from BALB/c mice were isolated following mechanic mincing and enzymatic digestion with collagenase.
(A) The BD IMag™ Mouse Dendritic Cell Enrichment Set was used for bulk selection, resulting in 35- and 29-fold enrichment of CD8α+ and CD8α– subsets of MHC II+CD11chigh conventional dendritic cells, respectively.
(B) Following bulk selection, CD8α+ and CD8α– subsets were sorted at 1,000 events/second in purity mode. Post-sort analysis revealed purity >99% for both sorted subsets.

-
BD FACSChorus™ FC Bead Lot Updater
-
Brochure
-
Quick Reference Guide
Request a Quote
Please fill in the following information and we will get in touch with you regarding your query.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.